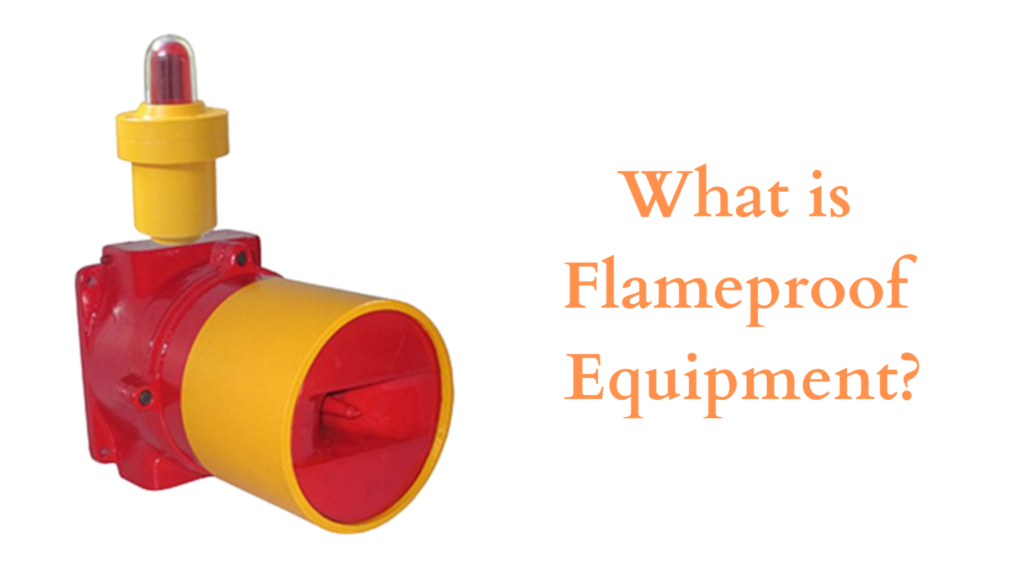
In industries where flammable gases, vapors, or dusts are present, even a single spark can lead to catastrophic accidents. To safeguard people, property, and processes, specialized flameproof (explosion-proof) equipment is essential.
Flameproof equipment is not just an engineering choice; it is a legal and safety requirement under international standards like ATEX, IECEx, and IS/IEC 60079. From oil refineries to fertilizer plants, thousands of installations depend on these certified devices to ensure uninterrupted and safe operations.
This comprehensive guide explains what flameproof equipment is, how it works, its certifications, types, applications, and why businesses in hazardous industries cannot afford to ignore it.
Flameproof equipment (also called explosion-proof equipment) is designed to:
Contain any explosion that may occur inside its enclosure.
Prevent ignition of the external atmosphere, even if sparks or flames are generated internally.
The principle is simple: if gases inside ignite, the flameproof enclosure is strong enough to withstand the explosion and cool escaping gases so they do not ignite the external atmosphere.
In technical terms, flameproof equipment complies with the Ex d (Flameproof/Explosion-Proof) protection method as per IS/IEC 60079-1.
It’s important to differentiate protection concepts:
| Protection Method | Ex Marking | Principle | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flameproof | Ex d | Contains and cools internal explosions | Motors, switchgear, lighting, junction boxes |
| Intrinsically Safe | Ex i | Limits energy (voltage/current) to prevent ignition | Instrumentation, sensors, transmitters |
| Increased Safety | Ex e | Adds insulation, creepage, design safety | Terminals, lighting, junction boxes |
👉 Flameproof (Ex d) is preferred for high-power devices like motors, lighting, control panels, where sparks are unavoidable.
Flameproof equipment is used according to hazardous area classification:
| Zone | Gas/Dust Presence | Typical Environment | Equipment Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zone 0 | Continuous presence of flammable gases/vapors | Inside fuel tanks | Intrinsically Safe (Ex i) |
| Zone 1 | Likely during normal operation | Refinery loading bay | Flameproof (Ex d) or IS |
| Zone 2 | Unlikely, and if present only for short duration | Petrol pump forecourt | Ex d, Ex e acceptable |
| Zone 20 | Continuous dust | Grain silos | Dust-tight Ex enclosures |
| Zone 21 | Dust likely in normal operation | Flour mill | Ex d / Dust-proof |
| Zone 22 | Dust presence abnormal | Packaging areas | Ex t / Ex p |
For petroleum & chemical plants, Zone 1 & Zone 2 are most relevant for flameproof electricals.
Different gases require different enclosure strengths:
| Gas Group | Example Gases | Risk Level | Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| IIA | Propane, Acetone | Lower | Standard flameproof enclosures |
| IIB | Ethylene, Coke Oven Gas | Medium | Stronger joints, tighter clearances |
| IIC | Hydrogen, Acetylene | Highest | Robust construction, strict tolerances |
The Flameproof Torch FI/RT/02, for example, is certified for IIA, IIB, and IIC, meaning it can be used in all high-risk industries.
Equipment must ensure its surface temperature never ignites the surrounding atmosphere:
| Temp Class | Max Surface Temp | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | 450°C | Methane, Propane |
| T2 | 300°C | Ethylene |
| T3 | 200°C | Gasoline, Diesel |
| T4 | 135°C | Acetaldehyde |
| T5 | 100°C | Hydrogen Sulfide |
| T6 | 85°C | Carbon Disulfide |
👉 Most flameproof lighting & torches are designed for T4–T6, ensuring safety even in hydrogen environments.
Flameproof equipment must comply with international and national regulations:
ATEX (Europe): Directive 2014/34/EU, marking Ex d IIC T4 Gb.
IECEx (Global): IEC 60079 standard certification scheme.
IS/IEC 60079 (India): Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) approval.
PESO/DGMS Certification (India): For petroleum, explosives, mining.
UL/FM (USA): Explosion-proof compliance for North America.
Always verify that equipment has valid Ex certification labels and up-to-date test reports.
Industries use a wide range of flameproof products, including:
Flameproof Lighting – floodlights, well glass fittings, emergency lights.
Flameproof Torches & Flashlights – rechargeable, Zone 1/2 certified.
Flameproof Junction Boxes & Control Stations – switches, MCBs, push buttons.
Flameproof Motors & Starters – pumps, compressors in hazardous areas.
Flameproof Signaling Devices – hooters, beacons, sirens.
Flameproof Process Instruments – transmitters, analyzers, sensors.
Flameproof Distribution Boards & Panels.
Flameproof equipment is mandatory in:
Oil & Gas Refineries
Petrol Pumps & Fuel Stations
Chemical & Fertilizer Plants
Pharmaceutical & Paint Factories
Power Generation (Coal & Gas)
Mining & Tunneling
Marine & Offshore Platforms
Food & Grain Storage (Dust Hazards)
Wherever ignitable atmospheres exist, flameproof gear is the frontline defense.
Safety Compliance with global standards
Worker Protection from fire & explosion hazards
Durability in harsh industrial environments
Reliability – minimizes downtime
Versatility – applicable across industries
Trust & Liability Protection – avoids regulatory fines and accidents
Costlier than standard electrical gear.
Heavier due to robust enclosures.
Requires certified installation & maintenance.
Still, benefits far outweigh limitations in high-risk industries.
Q1. What is the difference between flameproof and explosion-proof?
They are often used interchangeably. Both refer to equipment designed to contain internal explosions and prevent ignition of external atmospheres.
Q2. Is flameproof equipment mandatory in petrol pumps?
Yes, PESO mandates flameproof certified equipment for Zone 1 & Zone 2 hazardous areas in petrol stations.
Q3. What does Ex d IIC T6 Gb mean?
This is an Ex marking:
Ex d = Flameproof enclosure
IIC = Gas group (Hydrogen/Acetylene)
T6 = Max surface temp 85°C
Gb = Equipment protection level (high).
Q4. How often should flameproof equipment be inspected?
At least annually, and more frequently in highly corrosive or critical installations.
Q5. Can normal electrical equipment be modified to be flameproof?
No. Flameproof equipment must be manufactured and certified as such. Field modifications invalidate certification.
Q6. What is the lifespan of flameproof equipment?
Typically 10–15 years, depending on environment and maintenance.
Flameproof equipment is not an option — it is a safety necessity in hazardous industries. By choosing certified, durable, and reliable Ex d equipment, businesses protect lives, comply with regulations, and ensure smooth operations in explosive atmospheres.
📩 Contact Flameproof Instrumentation for BIS-certified, PESO-approved flameproof solutions across lighting, torches, junction boxes, and control gear.
Email: sales@flameproof.co.in | Phone: +91-9321160178
Emergency lighting designed for use in hazardous areas.
Provides illumination during critical situations without compromising safety.
Audible and visual signaling devices with flameproof features.
Essential for alerting personnel in the presence of danger.
Diverse range of flameproof lighting solutions for hazardous environments.
Includes various fixtures and designs to meet specific safety requirements.
Safety equipment designed with flameproof features.
Ensures protection against potential ignition sources in dangerous atmospheres.
Instruments and control devices certified as flameproof.
Facilitates safe and precise control of industrial processes within hazardous areas.
Various electrical components designed to operate safely in explosive atmospheres.
Ensures the integrity of electrical systems in critical settings.
Flameproof equipment is a critical component in safeguarding lives and assets in industries with flammable atmospheres. By understanding the principles, certifications, and differences between protection methods, businesses can make informed decisions, ensuring the highest level of safety in hazardous areas. Invest wisely, and prioritize safety.
